PROCESSES
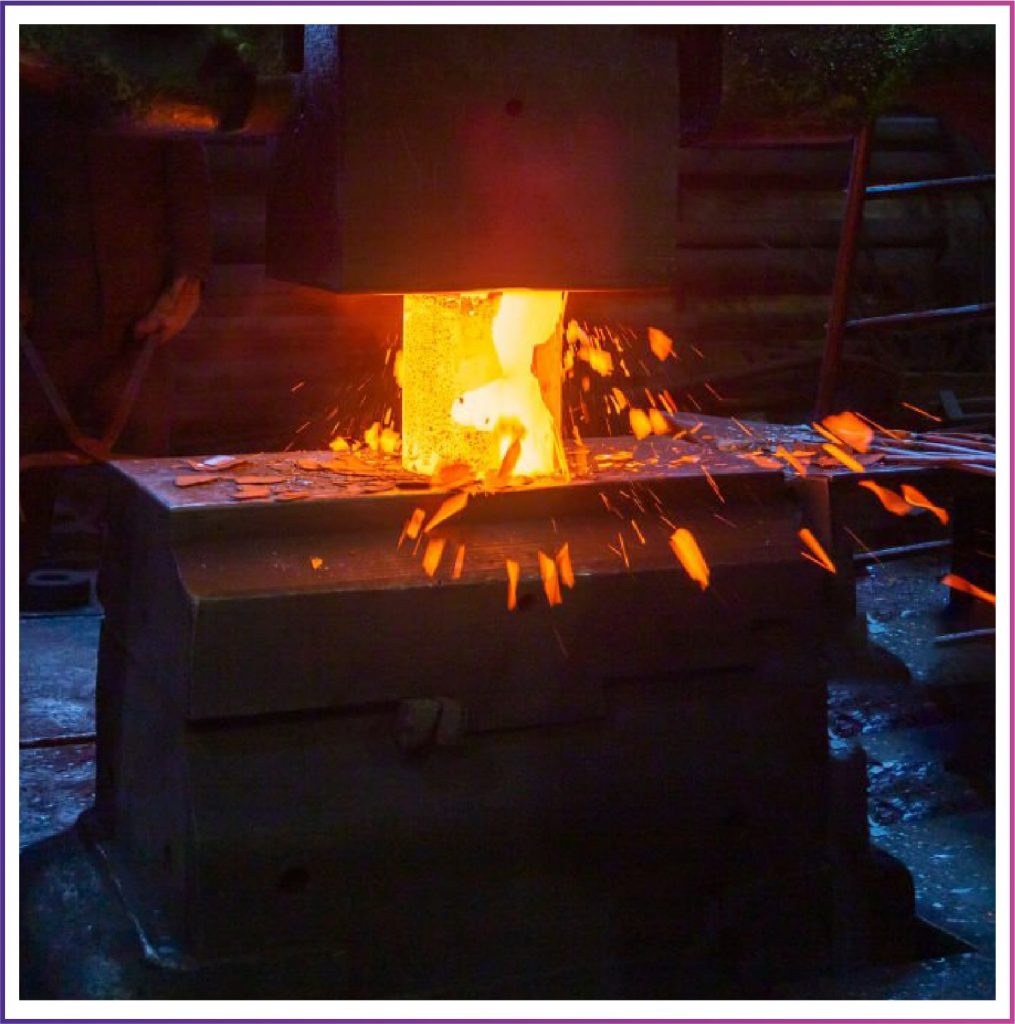
HOT FORGING
Hot forging is the common method for producing bolts with large diameters from thread sizes of M36 or more, and a length of 300 mm and more. Here, the bar stock is heated up to high temperatures to make the material more malleable and then fed into a forging press. Through Hot forging, it is possible to manufacture even complex shapes and high degrees of forming. A distinctive feature of hot-formed fasteners is their raw surface structure. While Hot forging is very time-consuming, is a chipless process unlike machining.

COLD FORGING
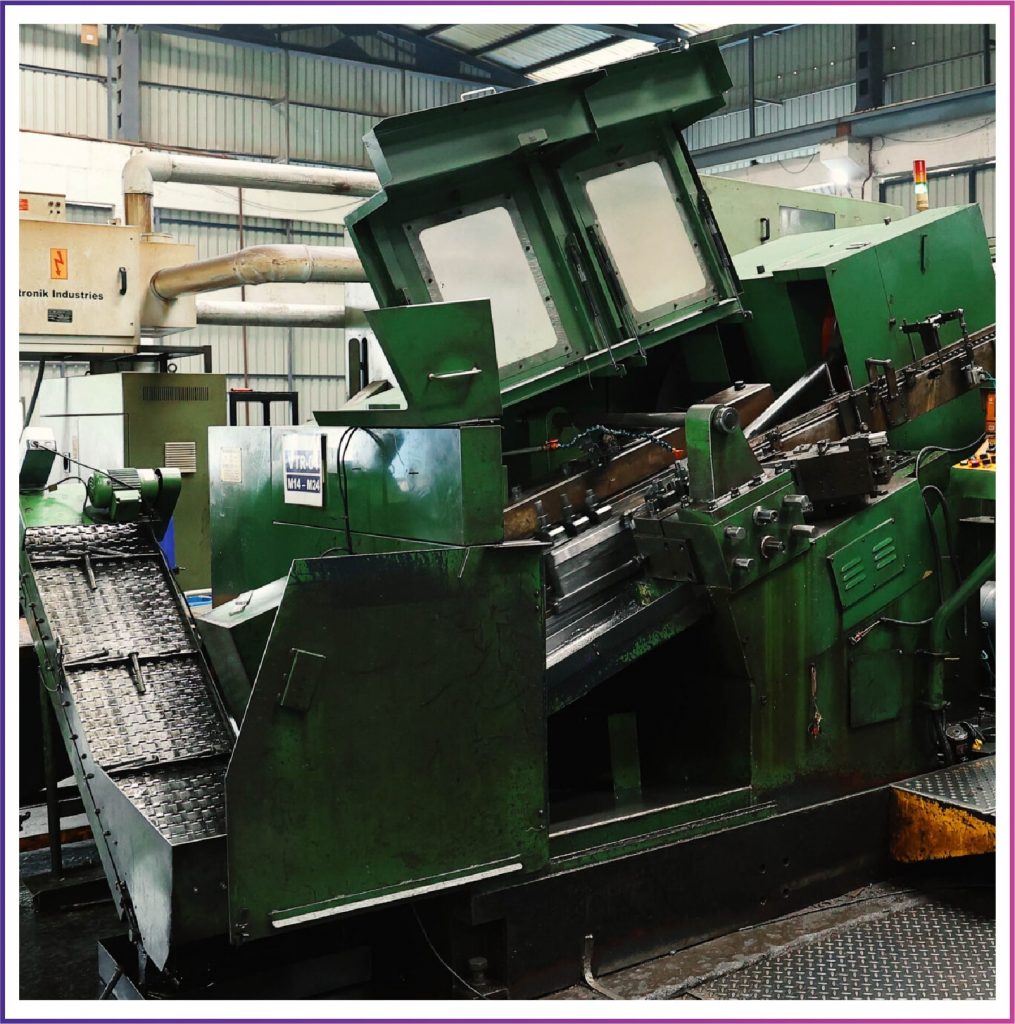
This method enables the high-speed manufacture of net shape parts or near net shape parts with favorable mechanical properties and a high-quality surface finish. During cold forging, the material’s crystal structure undergoes profound changes, becoming stronger and more resistant. The result is a finished part with better physical and mechanical properties.
In the Cold Forging process, the bar stock is inserted into a die and squeezed with a second closed die. The deformation starts at room temperature and changes the shape and size of the initial part until it has assumed the shape of the die.
At VK Fasteners, we offer a wide range of Cold forging fasteners, providing our customers with Consistent Quality, Faster Deliveries and Cost-Effective Solutions.

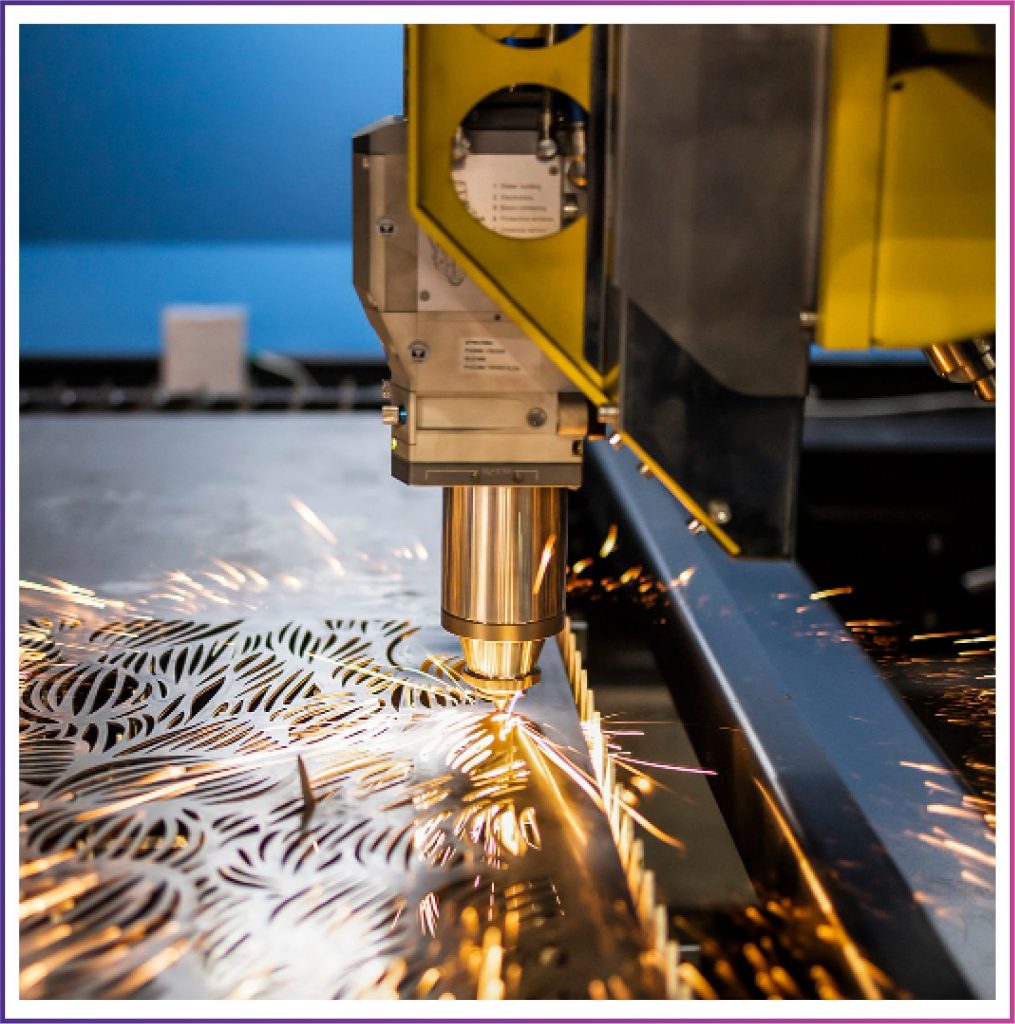
MACHINED COMPONENTS
Machined Components through CNC turning centres and machine centres ensuring highest degree of accuracy repeatability through demarked to life etc…
Machined parts are vital components in the manufacturing industry, playing a crucial role across various sectors in automotive, aerospace, electronics, machined parts are essential for the smooth functioning of complex systems. Modern manufacturing relies heavily on machined parts, which are carefully crafted using various techniques such as CNC Machining, turning, Milling, and grinding.

PROCEDURES TO CREATE
MACHINED PARTS
CNC machining is a popular and adaptable technique for creating machine
parts. It uses computer software to direct the movements of machining tools
like lathes, mills, or routers. CNC machining is known for its high accuracy,
quickness, and ability to produce intricate shapes.
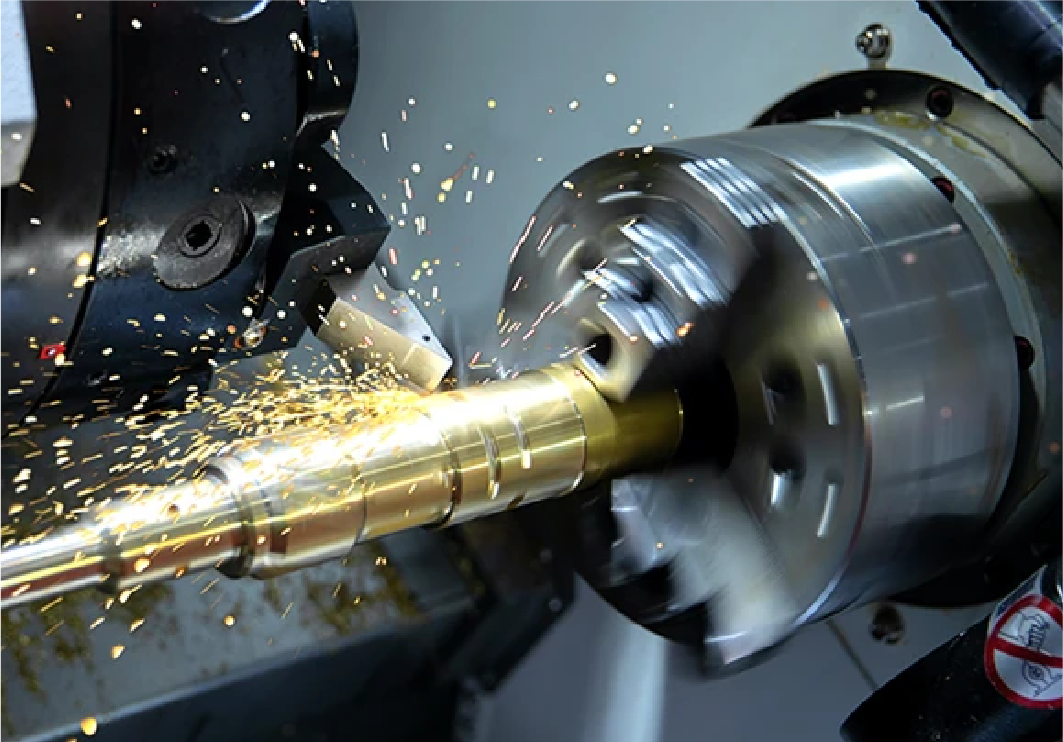

Turning
Turning is a machining process in which a workpiece rotates while a cutting tool removes material to create cylindrical or conical shapes. Lathes are commonly used for turning operations and are ideal for producing parts like shafts, bushings, and valves.
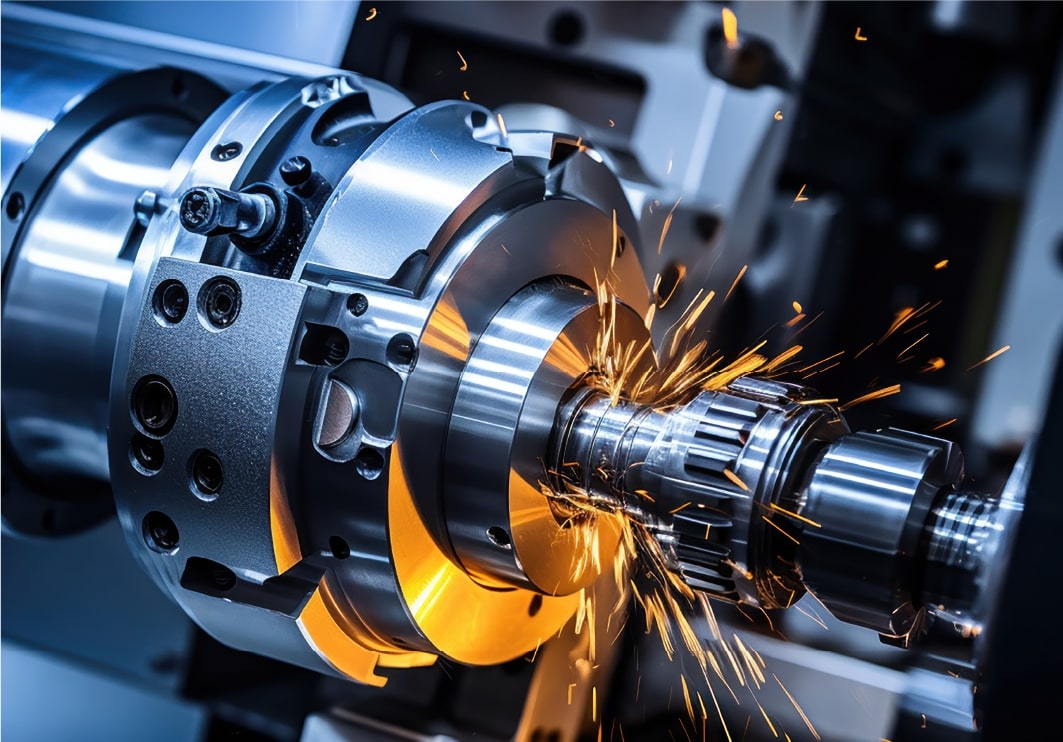

Grinding
Using abrasive wheels to remove material and achieve a high surface finish and dimensional accuracy. This process is used for fine-tuning machined parts and achieving tight tolerances.
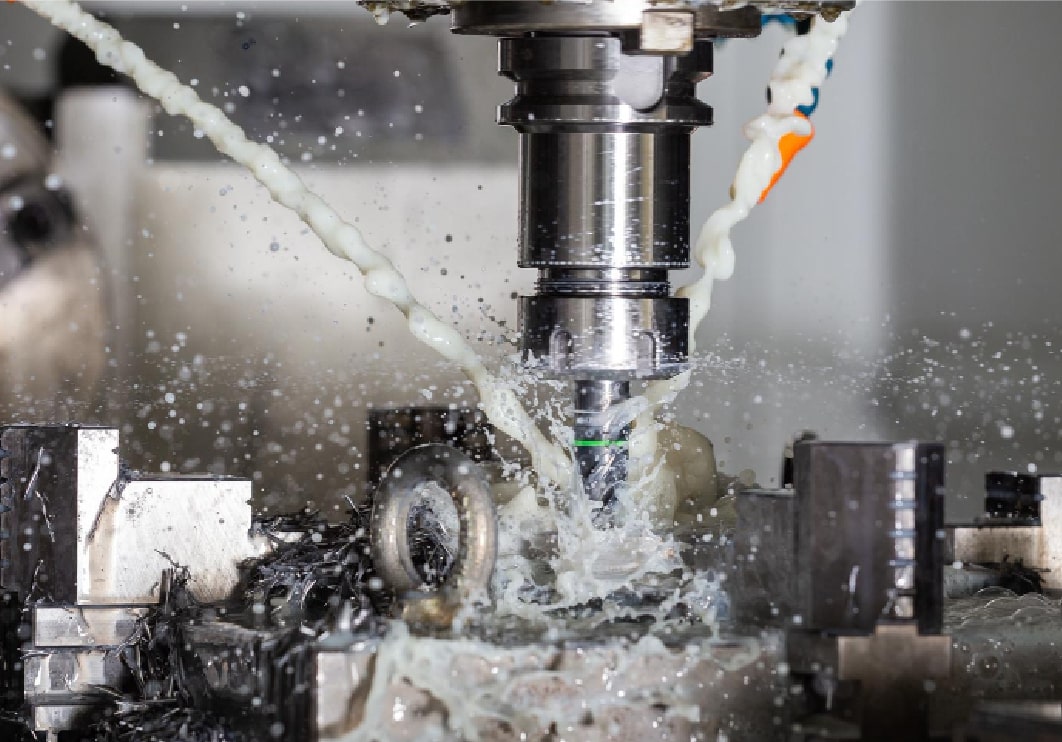

Milling
Milling utilizes rotary cutters to remove material from a workpiece, producing flat or contoured surfaces. This process is suitable for creating slots, holes, and complex 3D shapes. CNC mills provide advanced capabilities for precise milling operations.
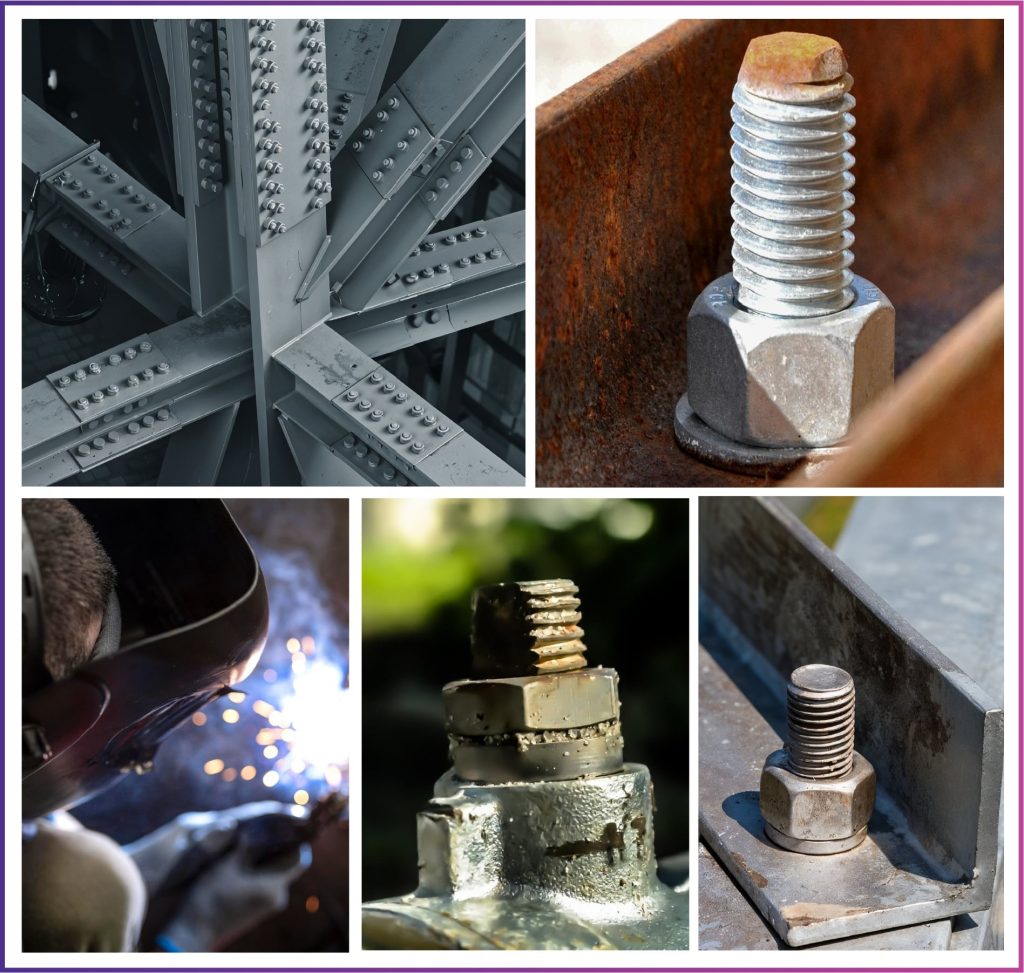
FEATURES
- High strength
- High resistance to stress corrosion cracking, corrosion fatigue, and erosion
- Good workability and weldability
- High interchangeability
- Thermal resistance & chemical resistance

APPLICATIONS
Pump & Value Industries

Aeronautical Industries & Earthmoving Equipment’s

Machinery Manufacturing Industries

Application in Instrumentation & Hydraulic & Pneumatic System
Automotive Industries

Medical & Pharmaceutical
Economizers

Condenser
Furniture Industries

Domestic Applications

Offshore Construction


